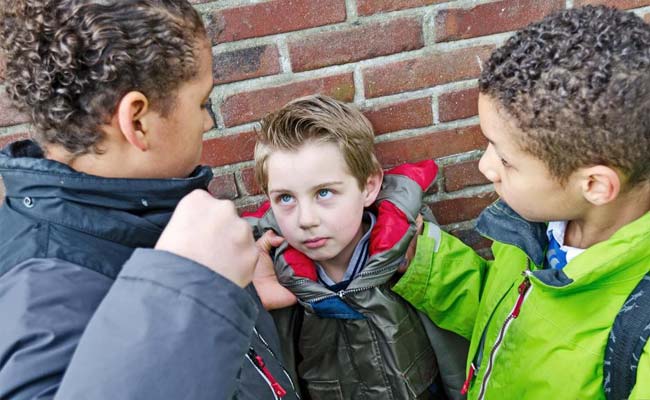
ndividual differences within the motivation to interact in or to keep away from competitive socialinteraction (bullying) are mediated by using the basal forebrain. (Representational Photograph)
New york: The brains of bullies’ are Stressed out to are seeking for Satisfaction from selecting onsufferers, a new Examine in mice has located.
Character differences within the motivation to engage in or to avoid competitive social interplay (bullying) are mediated via the basal forebrain, lateral habenula circuit within the brain, researchers said.
For the Examine, scientists from Icahn College of drugs at Mount Sinai inside the US targeted onidentifying the mechanisms by using which particular brain praise regions interact to modulate the motivational or rewarding thing of aggressive behaviour the use of a mouse model.
Maladaptive competitive behaviour is related to a number of psychiatric disorders and is concept to partlyend result from inappropriate activation of mind praise systems in response to competitive or violent social stimuli, researchers said.
“Our Look at is the first to demonstrate that bullying behaviour turns on a number one mind praise circuit that makes it pleasing to a subset of people,” stated Scott Russo from Icahn School.
“Furthermore, we display that manipulating activity in this circuit alters the pastime of mind cells andultimately, aggression behaviour,” stated Russo.
To Have a look at Character differences in aggressive behaviour, researchers mounted a mouse behavioural model that exposed grownup men to a younger subordinate mouse for three minutes each day for 3 consecutive days, and located that 70 per cent of mice exhibited competitive behaviour (AGGs)even as 30 in line with cent of mice showed no aggression in any respect (NONs).
the usage of conditioned area desire, a way commonly used in animal research to evaluate possibilitiesfor environmental stimuli which have been related to a high quality or poor reward, researchers locatedthat AGGs mice bullied/attacked the subordinate mouse and sooner or later developed a conditioned regiondesire for the intruder-paired context, suggesting that the aggressive mice located the potential to subordinate another mouse profitable.
Conversely, NONs mice did now not bully/assault the intruder mouse and in the end evolved a conditionedlocation aversion, researchers stated.
using electrophysiological and histological techniques, researchers discovered that when exposed to theopportunity to bully another Individual, AGGs mice exhibit extended interest of the basal forebrain gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) projection neurons that lessen activity inside the lateral habenula, a place of the mind that would generally encode an aversion to competitive stimuli.
discovered at some stage in the brain and produced by using neurons, GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that binds to GABA receptors, making the neighbouring neuron less excitable.
Conversely, researchers located NONs exhibit decreased basal forebrain activation and a subsequentboom in lateral habenula neuronal firing, which makes the aggression stimuli aversive.
The findings have been posted inside the journal Nature.
(This tale has not been edited by means of NDTV workforce and is automobile-generated from a syndicated feed.)